

 | Next: Bibliography |
Relative advantages of the modular system
i.e. possible door-to-door
transport
![]() higher usage.
higher usage.
Allows profitable application to the most diverse
transport requirements.
![]() the majority of the invested capital (Carrier+Track)
can work during a great part of the day.
the majority of the invested capital (Carrier+Track)
can work during a great part of the day.
Newly developed transport technologies can be
integrated in the MAIT network.
![\includegraphics[width=40mm]{fig_victoria.ps}](img46.gif) At night: freight-transport
At night: freight-transport
![\includegraphics[width=40mm]{fig_delivery.ps}](img47.gif)
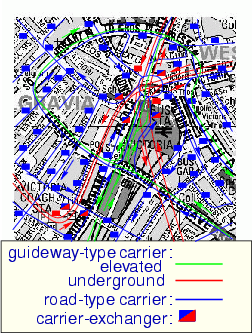
The figure shows a possible MAIT network around Victoria station,
London, UK. It sill needs to be verified by computer simulation
whether such a network can actually cope with the enormous amount of
traffic at this point. However, it gives an imagination on how
different carrier types (here road- and guideway carriers) can
interact via carrier exchangers to represent a seamless
transportation network. Note that there are stops of the road
carrier network (blue squares) in front of almost every building.
Flexible solutions for a transient phase
as public transport.
faster inter-city lines
refined by street-carriers.
during a transient phase, cabins could be loaded on conventional
transport systems
i.e. trains or ships.
Problems with the modular approach
![]() Minimisation by optimization of logistics.
Minimisation by optimization of logistics.
![]() Minimisation by optimization of network topology and
choice of carrier technology.
Minimisation by optimization of network topology and
choice of carrier technology.
![]() optimization by
optimization by
The total number of carriers without cabins is called the carrier overhead .



Next: Bibliography

MAIT home
Last updated: 2001-05-30 by
webmaster@maitint.org